Demineralizers
Demineralizers or ion exchangers are equipments which can hold ion exchange resins. Different type of demineralizers are used for water purification.
Dissolved impurities and foreign particles entrained in power plant fluid systems generate corrosion problems and decrease the heat exchanger efficiency as a result of fouling of relevant heat exchanger surfaces. Demineralization of water is one of the most commonly used processes to remove dissolved impurities.
Demineralizers or ion exchangers are equipments which can hold ion exchange resins. Demineralization or ion exchange refers to exchange of ions between a solid substance (called a resin) and an aqueous solution (makeup water). Ion exchange resins consist of very small beads, termed resin beads, having an average diameter of 0.010 millimeters or less.
After a certain period of time, ion exchange resins are exhausted and they have to be regenerated. During regeneration, an acid solution (for cation exchange units) and a caustic solution (for anion exchange units) is used, properly diluted with water, which is typically distributed above the resins. Regeneration is usually a multi-step process, also involving backwashing and rinsing stages in order to remove any entrained particles.
Demineralised water is produced via three main routes:
- Via Ion-exchange process using Ion exchange resins: Positive ions are replaced by hydrogen ions and negative ions are replaced by hydroxide ions.
- Via Electro-Deionisation also an Ion-exchange process takes place: An electric current is sent through the resins to keep them regenerated. The unwanted ions move away from the reaction surface to the electrodes.
- Via Membrane filtration: most times in multiple steps
Demineralised water is used for industrial and scientific purposes. You can think of the following applications:
- Laboratory applications and testing
- Carwash
- Wash water for computer chip manufacture
- Automotive uses eg. lead-acid batteries and cooling systems
- Boiler feed
- Laser cutting
- Optimisation of fuel cells
- Steam irons and steam raising applications
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Cosmetics
- Aquariums
- Fire extinguishers
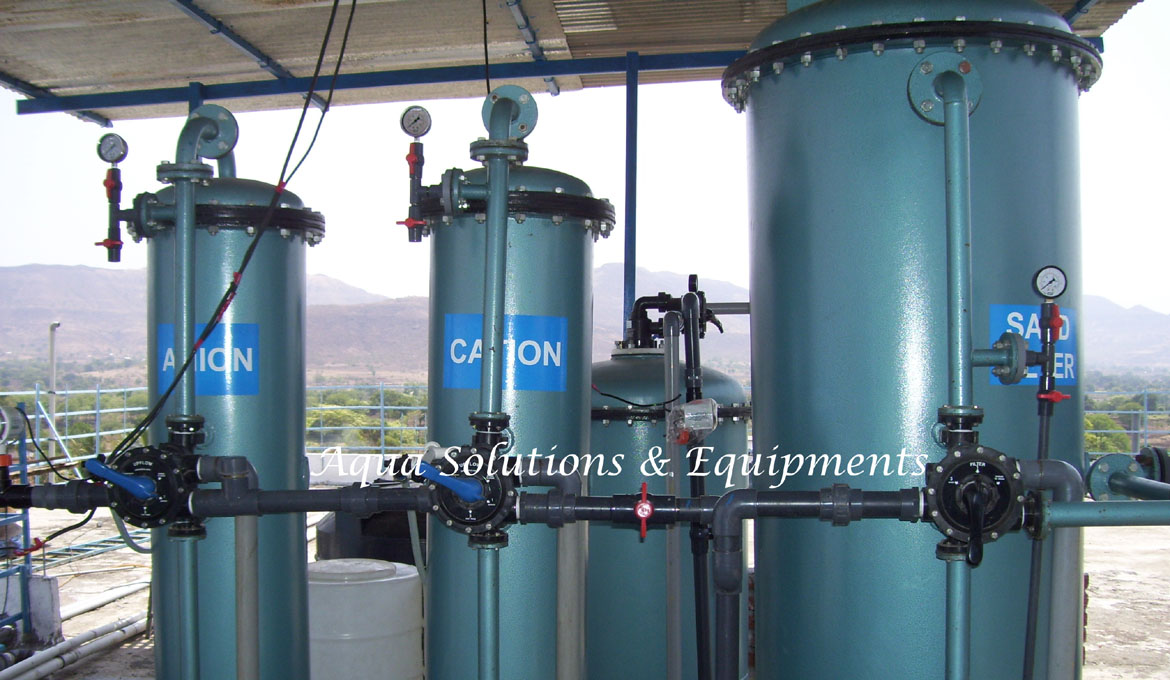
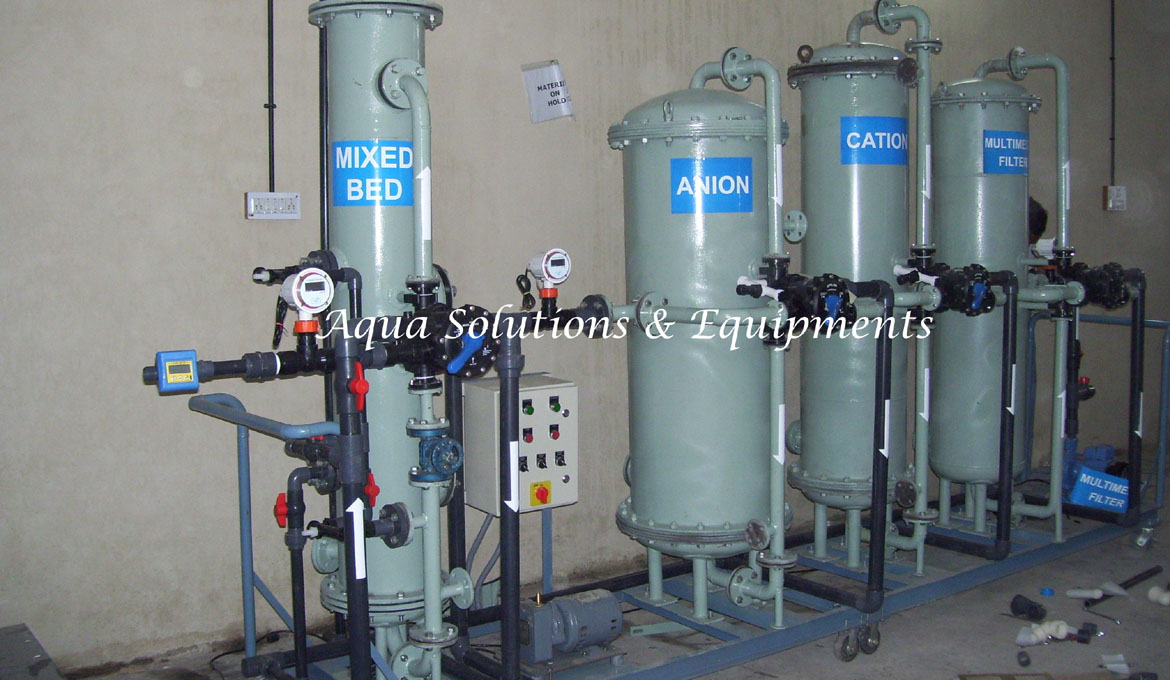
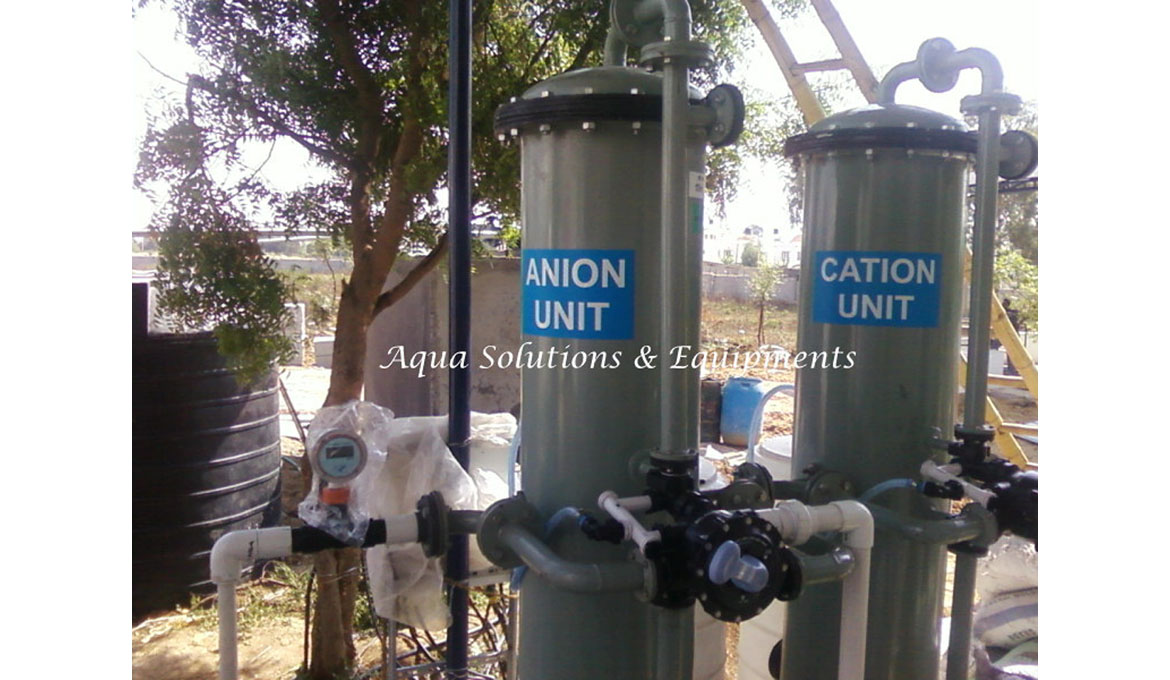
Types of Demineralizers or Ion Exchangers
A Single-Bed Demineralizer contains either cation resin elements (a cation is an ion with a positive charge: common cations include Ca++, Mg++, Fe++, and H+) or anion resin elements (an anion is an ion with a negative charge: common anions include Cl-, SO-, and OH-). Consequently, a cation resin is one that exchanges positive ions, whereas an anion resin is one that exchanges negative ions. Impurities in plant water are replaced with hydrogen ions in the cation bed and hydroxyl ions in the anion bed. The hydrogen ions and the hydroxyl ions then combine to form pure water.
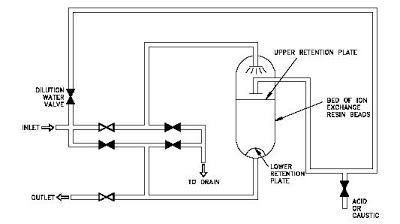
Single-Bed Demineralizers are usually regenerated "in place." The resins are not pumped out to another location for regeneration. The regeneration process is the same for cation beds and for anion beds; only the regenerating solution is different. It is important to realize that if the ion exchanger has been exposed to radioactive materials, the backwash, regeneration, and rinse solutions may be highly radioactive and must be treated as a radioactive waste.
A Mixed-Bed Demineralizer is a demineralizer in which the cation and anion resin beads are mixed together. It is equivalent to a number of two-step demineralizers in series. In this type of demineralizer, more impurities are replaced by hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, and the water that is produced can be extremely pure. The conductivity of the produced water can therefore be 0.05 μS/cm or even less. Regeneration of a mixed bed demineralizer is generally more complicated than for a single bed demineralizer.

Some Mixed-Bed Demineralizers are designed to be regenerated externally, with the resins being removed from the vessel, regenerated, and then replaced. With this type of demineralizer, the first step is to sluice the mixed bed with water (sometimes assisted by air pressure) to a cation tank in a regeneration facility. The resins are backwashed in this tank to remove suspended solids and to separate the resins. The anion resins are then sluiced to an anion tank. The two batches of separated resins are regenerated by the same techniques used for single-bed ion exchangers. They are then sluiced into a holding tank where air is used to remix them. The mixed, regenerated, resins are then sluiced back to the demineralizer.








